Cell Cycle











Cell Cycle
Cell division is an essential process in all living organisms. The mode of cell division is fundamentally similar in all organisms, During the process of division a cell, the processes like DNA replication and cell growth must take place in a sequential and coordinated manner to ensure the correct division and formation of progeny cells with intact genomes.
Cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events or a set of stages by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesize the other constituents (important for the cell) of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells.
In terms of cytoplasmic increase, cell growth is a continuous process, DNA synthesis occurs during a specific stage of the cell cycle only. The DNA (chromosomes) are further distributed to daughter nuclei by a series of events. All these events are well-coordinated and are under genetic control.
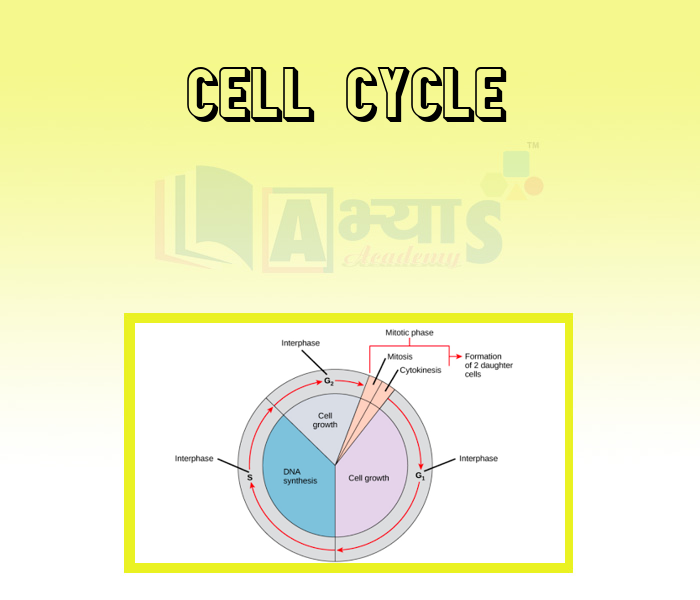
Phases of Cell Cycle :
A typical eukaryotic cell (human cell) divides once in every 24 hr. This duration of cell cycle can vary from an organism to other organism and also from one cell type to another. e.g., yeast cell progresses through the cell cycle and divides in only about 90 min.
i) Interphase: It is the period between the end of one cell division to the beginning of the next cell division, i.e., (between two successive M-phase).
During this phase, cell prepares itself for both cell growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. So, it is also known as preparation phase. It lasts for about 90-96%, i.e., more than 95% of the total duration of cell cycle. In a cell cycle of human cell, only about one hour is taken by the dividing phase out of 24 hours duration of one cell cycle.
Interphase is further divided into following three sub stages on the basis of various synthetic activities.
(a) (Gap - 1) - Phase (b)
(Synthesis) - phase
(c) (Gap - 2) - Phase
- phase (Quiescent Stage)
ii) M - Phase : - Following the interphase, the cell enters the M - Phase or mitotic phase.
MITOSIS : - In this type of division, the chromosomes replicate themselves and get equally distributed into daughter nuclei, i.e., the chromosome number in the parental and progeny cell (diploid) becomes the same. Therefore, it is also known as equational division.
Mitosis is also known as somatic cell division because it always occur in somatic cells. Mitotic cell division is seen in the diploid somatic cells in animals, whereas, in plants, mitotic division is seen in both haploid and diploid cells. It is known to be the phase of actual cell division, which starts with the division of nucleus, followed by the separation of daughter chromosomes, i.e., karyokinesis and terminates with the cytoplasmic division, i.e., cytokinesis.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
